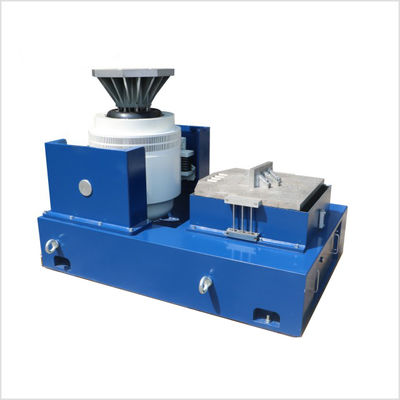
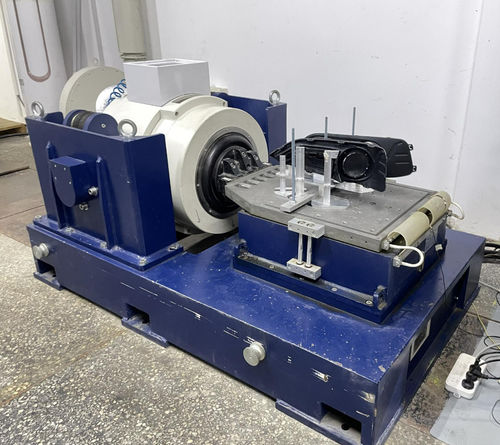
En Dongguan Precision Test Equipment Co., Ltd., nuestro compromiso se extiende más allá de proporcionar equipos de prueba de vibración de alta calidad.Nos dedicamos a asegurar que nuestros clientes experimenten el más alto nivel de satisfacción a través de un servicio integral después de las ventasEsto incluye el mantenimiento experto, la reparación eficiente y los valiosos servicios de actualización para una amplia gama de sistemas de prueba de vibración.
Como empresa de alta tecnología especializada en la fabricación de agitadores electrodinámicos, agitadores hidráulicos, amplificadores de potencia,y controladores de vibración y orgullosos de ser la primera empresa nacional con investigación y desarrollo interno y producción de estos tres componentes centrales nuestros productos son de confianza de las empresas líderesNuestro alcance se extiende a Rusia, América del Norte, Japón, Oriente Medio y más allá.
Con más de una década de esfuerzo dedicado, nos hemos convertido en una empresa de tecnología integral que integra I+D, producción, ventas y, lo más importante, servicio.Nuestro experimentado equipo de postventa está equipado para proporcionar un mantenimiento profesional, servicios de reparación y actualización para diversas marcas internacionales de renombre como LDS (Reino Unido), UD (EE.UU.), LING (EE.UU.), TIRA (Alemania), B&K (Dinamarca), IMV (Japón), SHINKEN (Japón) y KOKUSAI (Japón),así como las marcas nacionales de agitadores de vibración, amplificadores de potencia y controladores de vibración.
Nuestras ofertas de servicios integrales:
Entendemos el papel crítico que juegan los sistemas de pruebas de vibración en sus operaciones.
Servicios de agitadores de vibración:
Mantenimiento, reparación y sustitución de armaduras:Cuidados expertos para el componente móvil central de su agitador, asegurando su integridad y rendimiento.
Mantenimiento, reparación y reemplazo de la bobina de excitación:Abordando problemas con el corazón electromagnético del agitador.
Reemplazo de piezas de desgaste:Reemplazo oportuno de los componentes consumibles como las placas de tracción de PP, las ruedas de guía inferiores, las botas de polvo, los fusibles, el aceite hidráulico anti-desgaste, las mangueras de aire y los conductos de ventilación.
Mantenimiento, reparación y sustitución de la mesa de deslizamiento horizontal:Asegurar un ensayo de vibración horizontal suave y preciso.
Reemplazo del cable de sensores y del cable BNC:Abordar los problemas de transmisión de señales con reemplazos de alta calidad.
Opciones de expansión de la cabeza:Proporcionar soluciones para adaptarse a muestras de ensayo más grandes.
Mantenimiento mecánico completo:Servicio general de los componentes mecánicos del agitador para un funcionamiento óptimo.
Servicios de amplificadores de potencia (aspectos eléctricos):
Mantenimiento, reparación y sustitución del módulo del amplificador de potencia:Abordar los problemas a nivel de componentes para una entrega eficiente de energía.
Mantenimiento, reparación y sustitución del módulo de control del amplificador de potencia:Asegurar el correcto funcionamiento de la electrónica de control del amplificador.
Mantenimiento eléctrico completo:Servicio general de los sistemas eléctricos del amplificador para un rendimiento fiable.
Servicios de control de vibraciones:
Calibración y eliminación de polvo de los canales:Manteniendo la precisión y la longevidad de los canales de entrada de su controlador.
Solución de problemas de entrada, comunicación, salida y fallas de energía:Diagnóstico y resolución eficientes de los fallos de funcionamiento del controlador.
Adiciones de características de software y actualizaciones/reemplazos de hardware:Mejorando las capacidades y extendiendo la vida útil de su controlador.
Nuestro compromiso con la satisfacción del cliente:
Nuestro principio básico es proporcionar los productos y servicios más satisfactorios a nuestros valiosos clientes.y ofreciendo actualizaciones de softwareAdemás, hacemos hincapié en la importancia del mantenimiento proactivo.desempeñamos un papel crucial en la prevención de posibles problemas y garantizar el funcionamiento continuo de sus sistemas de prueba de vibraciónPoseemos las amplias capacidades de ingeniería para la inspección del sistema, mantenimiento y manejo rápido de fallos.Estamos comprometidos a ofrecer un servicio superior..
¿Por qué elegir Dongguan Precision para sus necesidades de servicio?
Profesionales con experiencia:Nuestro equipo de posventa está compuesto por profesionales de servicio técnico experimentados con más de 20 años de experiencia en la industria de pruebas de vibración,especializada en el mantenimiento y reparación de varias marcas de equipos de prueba de vibración.
Respuesta rápida:Entendemos la urgencia de minimizar el tiempo de inactividad. Ofrecemos respuestas en línea dentro de 30 minutos, organizamos servicio en el sitio dentro de 2 horas, y nuestro objetivo es llegar a su ubicación dentro de 24 horas.
Calidad de servicio eficiente:Nuestro personal de servicio da prioridad a sus necesidades de producción, utilizando su amplia experiencia y métodos científicos para diagnosticar y resolver rápidamente las causas comunes de fallas.
Nuestros servicios en detalle:
Servicios de reparación:Cuando su equipo funcione mal, póngase en contacto con nosotros de inmediato. Haremos arreglos para que un ingeniero de servicio técnico profesional proporcione un diagnóstico en línea en 30 minutos. Una vez que se identifique el problema,Enviaremos un técnico para reparación en el sitio y reemplazo de componentes.
Servicios de mantenimiento y mantenimiento:Desarrollamos planes científicos de mantenimiento periódico, incluido el reemplazo regular de piezas de desgaste y proporcionamos orientación experta sobre el uso diario óptimo de su equipo.
Servicios de actualización de software:Manténgase al día con nuestra actualización de software y soporte de mejora de características.
Confíe en Dongguan Precision para mantener sus sistemas de prueba de vibración funcionando al máximo rendimiento, asegurando la fiabilidad y precisión de sus procesos de prueba.Póngase en contacto con nuestro equipo de servicio hoy para discutir su mantenimiento, reparación, o las necesidades de mejora.
Encontrar mensajes de error como "Open Loop", "Drive Max", o "Gain Limit" durante las pruebas de vibración puede detener su progreso y causar frustración.Entendemos la importancia de resolver problemas rápidamenteEsta guía describe siete pasos clave que puede seguir para diagnosticar y resolver estos problemas comunes antes de escalar a investigaciones más complejas.
Cuando el software de control de vibraciones señala estos errores, normalmente indica una discrepancia entre la salida comandada y la capacidad del sistema para lograrla.Siga estos pasos para identificar sistemáticamente la causa raíz:
Siete pasos para solucionar los errores "Open Loop", "Drive Max" y "Gain Limit":
1Verifique la ganancia del amplificador de potencia:
El control:Asegúrese de que el control de ganancia en su amplificador de potencia está adecuadamente ajustado (es decir, se ha encendido lo suficiente).el amplificador puede no estar proporcionando suficiente energía para conducir el agitador a los niveles deseados.
Acción:Aumente gradualmente la ganancia en el amplificador de potencia. Consulte el manual de su sistema para los ajustes de ganancia de inicio recomendados. Tenga cuidado de no aumentar excesivamente.que podría conducir a la sobrecarga del agitador.
2Inspeccionar los cables de interconexión:
El control:Examine cuidadosamente todos los cables que conectan el controlador de vibración, el agitador de vibración (mesa de vibración) y el amplificador de potencia.
Acción:Asegúrese de que todos los cables estén conectados de forma segura a los puertos correctos en ambos extremos.Preste mucha atención al cable de señal de accionamiento del controlador al amplificador y al cable de señal de retroalimentación del acelerómetro al controlador.
3Confirmar conexión de sensor y configuración de canal de entrada:
El control:Compruebe que el acelerómetro (sensor de vibración) está correctamente conectado al canal de entrada apropiado del controlador de vibración.
Acción:Verifique dos veces la conexión física del cable del sensor. En el software de control de vibración, revise la configuración del canal de entrada del acelerómetro. Asegúrese de que el modo de acoplamiento (por ejemplo, CA, CC,IEPE) está configurado correctamente para que coincida con el tipo de acelerómetro que está utilizandoUn ajuste incorrecto del acoplamiento puede impedir que el controlador reciba una señal de retroalimentación válida.
4Compruebe la señal del sensor:
El control:Determine si el acelerómetro realmente está emitiendo una señal.
Acción:Utilice la función "Previsualización de pruebas" o "Monitor" dentro de su software de control de vibraciones para ver la señal de dominio temporal del canal de entrada conectado al acelerómetro.Mientras observa la pantalla del softwareSi el sensor funciona y está correctamente conectado, debería observarse un cambio correspondiente en la señal de dominio temporal.Si no hay señal, el sensor en sí, su cable o el canal de entrada del controlador pueden estar defectuosos.
5. Evaluación del ruido del sistema y nivel previo a la prueba:
El control:Análisis del nivel de ruido del sistema y comparación con el nivel de salida inicial de su ensayo.
Acción:Durante la "Previsualización de prueba", observar el valor RMS (Radice media cuadrada) del ruido del sistema en el canal de entrada.comprobar la configuración del nivel previo a la prueba en el espectro objetivo o el perfil de prueba (a menudo un valor predeterminado del 10%)Si el nivel de ruido previo a la prueba es inferior al doble del valor de ruido RMS, el controlador puede tener dificultades para establecer un circuito de control estable debido a la baja relación señal-ruido.
Solución:Aumentar el nivel previo al ensayo en la configuración del software a un valor significativamente superior (al menos dos veces) al RMS de ruido del sistema medido.Esto proporciona al controlador una señal inicial más fuerte para trabajar con.
6. Ejecutar el control-amplificador de prueba de retorno:
El control:Prueba de la integridad de la trayectoria de la señal desde el canal de salida del controlador hasta el amplificador de potencia.
Acción:Desconecte temporalmente el cable que normalmente corre desde la salida de la unidad del controlador hasta la entrada del amplificador de potencia.Conectar este mismo cable directamente desde el canal de salida de la unidad del controlador a uno de los canales de entrada del controlador (el mismo tipo que utiliza para su retroalimentación acelerómetro). Configurar una prueba de circuito cerrado simple en el software utilizando este canal de entrada como fuente de retroalimentación. Ejecutar una barrida sinusoidal de bajo nivel o prueba de frecuencia fija.Si este ensayo de bucle autocerrado funciona normalmente, indica que los canales de salida e entrada del controlador, así como el cable de conexión, probablemente funcionan correctamente.Esto ayuda a aislar posibles problemas con el amplificador de potencia o la conexión entre el amplificador y el agitadorRecuerde volver a conectar los cables a su configuración original después de este ensayo.
7Revisa el nivel de espectro objetivo, la ganancia del amplificador y los límites de accionamiento:
El control:Si el error "Drive Max" persiste después de comprobar las conexiones físicas y la funcionalidad del sensor, examinar la configuración del software relacionada con el nivel de salida deseado y la ganancia del amplificador.
Acción:
Nivel de espectro objetivo:Asegúrese de que la amplitud general o el nivel definido en el espectro objetivo (para ensayos aleatorios o de choque) o la amplitud programada (para ensayos sinusoidales) no sean excesivamente altos,Demandando más salida de la que el sistema puede ofrecer con la configuración de ganancia del amplificador actualReduzca el nivel objetivo si es necesario.
La ganancia del amplificador:Si el nivel del espectro objetivo es alto, es posible que deba aumentar la ganancia del amplificador para proporcionar una señal de accionamiento suficiente.
Límites de la unidad de software:Compruebe la configuración de "Límite de accionamiento" en su software de control de vibraciones. Estas configuraciones evitan que el controlador envíe una señal de accionamiento demasiado grande al amplificador.Si el límite de accionamiento está demasiado bajo, podría estar restringiendo prematuramente la salida incluso si el amplificador tiene más espacio en la cabeza.manteniéndose dentro de los parámetros de funcionamiento seguros de su sistema.
Al trabajar sistemáticamente a través de estos siete pasos, usted puede efectivamente solucionar problemas comunes "Open Loop", "Drive Max"," y "Límite de ganancia" errores en su software de control de vibración y conseguir sus pruebas de vibración de nuevo en el caminoSi el problema persiste después de estas comprobaciones, se recomienda consultar al equipo de soporte técnico de Dongguan Precision para obtener asistencia más profunda.
Encontrar problemas de comunicación entre el controlador de vibración y el ordenador operativo puede ser un obstáculo frustrante antes de iniciar pruebas de vibración cruciales.Si se encuentra con un mensaje de error "dispositivo USB no se encuentra" al iniciar el software de control de vibración VCSEn Dongguan Precision Test Equipment Co., Ltd., hemos compilado una guía sencilla de solución de problemas para ayudarle a identificar y resolver rápidamente las posibles causas.
El enlace de comunicación principal entre el controlador de vibración y el ordenador es típicamente una interfaz USB 2.0.Aquí están las razones comunes detrás de este problema y cómo abordarlos:
Posibles causas y soluciones:
1Conexión USB física:
¿ Por qué?El paso más básico es asegurarse de que el cable de comunicación USB esté físicamente conectado de forma segura entre el controlador de vibración y el ordenador.
Solución:Inspeccione cuidadosamente ambos extremos del cable USB y asegúrese de que estén firmemente conectados a los puertos USB designados tanto en el controlador como en el ordenador.
2Conectores USB sueltos:
¿ Por qué?Incluso si se conectaron inicialmente, los conectores USB en ambos extremos del cable podrían haberse aflojado o desalojado parcialmente.
Solución:Mueva suavemente los conectores USB en ambos extremos del controlador y el ordenador. Si hay alguna jugada, empuje con firmeza hasta que estén sentados con seguridad.Una conexión débil puede interrumpir la comunicación de forma intermitente.
3Estado de energía del controlador:
¿ Por qué?El controlador de vibración debe estar encendido para que la computadora lo reconozca como un dispositivo conectado.
Solución:Compruebe el interruptor de alimentación en el controlador de vibración, asegúrese de que esté en la posición "ON", y busque las luces indicadoras de alimentación en el controlador para confirmar que está recibiendo energía.
4. Desaparecido o incorrecto controlador de hardware:
¿ Por qué?La computadora requiere controladores de hardware específicos (a menudo etiquetados como "Dispositivo USB 2.0" o similares) para comunicarse con el controlador de vibración.el controlador no será reconocido.
Solución:
Compruebe el administrador de dispositivos:Abra el Administrador de dispositivos en su computadora (busque " Administrador de dispositivos " en la barra de búsqueda de Windows).Busque cualquier dispositivo que aparezca en la lista de "Controllers Universal Serial Bus" o "Otros dispositivos" con un signo de exclamación amarillo o un signo de interrogaciónEsto indica un problema con el conductor.
Reinstalar el controlador:Si se encuentra tal entrada, haga clic derecho en ella y seleccione "Desinstalar dispositivo". Luego, desconecte el cable USB del ordenador, espere unos segundos y vuelva a conectarlo.Windows debería intentar volver a instalar el controlador automáticamente.
Instalación manual:Si la instalación automática falla,Es posible que deba instalar manualmente el controlador desde el soporte de instalación del software que viene con el controlador de vibración o descargar el controlador más reciente del sitio web del fabricante (e.g., sección de soporte de Dongguan Precision). Siga las instrucciones de instalación proporcionadas.
5Interferencia del software de vigilancia de virus:
¿ Por qué?En algunos casos, el software de monitoreo de virus demasiado agresivo puede identificar erróneamente el controlador de hardware para el controlador de vibración como una amenaza potencial y bloquear su instalación o operación.
Solución:
Deshabilitar temporalmente el monitoreo de virus:Como paso para solucionar problemas, desactive temporalmente su software de monitoreo de virus.
Reinstalar el controlador:Después de desactivar el software, intente volver a instalar el controlador de hardware para el dispositivo USB 2.0 como se describe en el punto 4.
Conducción/dispositivo de la lista blanca:Si el problema se resuelve después de desactivar el antivirus,Tendrá que configurar su software de monitoreo de virus para "lista blanca" el controlador de hardware del controlador de vibración o el propio dispositivo USB para evitar interferencias futurasRecuerde volver a activar su software de monitoreo de virus después de este paso.
6Puerto USB de computadora defectuoso:
¿ Por qué?Es posible que el puerto USB de su computadora que está utilizando para conectar el controlador de vibración esté defectuoso.
Solución:
Pruebe con otro puerto USB:Desconecte el cable USB del puerto actual e intente conectarlo a otro puerto USB de su computadora.
Reinstale el controlador (con el puerto nuevo):Después de conectarse a un puerto diferente, permita que Windows intente la instalación automática del controlador. Si no lo hace, vuelva a instalar el controlador manualmente como se describe en el punto 4.Esto ayudará a determinar si el problema se encuentra con un puerto USB específico.
Al comprobar sistemáticamente estas posibles causas, usted debe ser capaz de identificar y resolver el error "dispositivo USB no se encuentra" y establecer una conexión exitosa con su controlador de vibración,lo que le permite continuar con sus pruebas de vibración crucialesSi continúa experimentando problemas después de intentar estos pasos, no dude en consultar al equipo de soporte técnico de Dongguan Precision para obtener más ayuda.
En el ámbito de las pruebas de vibración, elacelerómetroactúa como el órgano sensorial crucial de su sistema de prueba de vibración. Es un transductor que convierte la cantidad física de vibración (aceleración e indirectamente relacionada con el sonido) en una señal eléctrica medible, proporcionando la entrada esencial para el análisis y el control. En Dongguan Precision Test Equipment Co., Ltd., enfatizamos la importancia de la instalación y el uso adecuados del acelerómetro para obtener datos de vibración confiables y significativos.
Los acelerómetros son la opción preferida para la medición de la vibración debido a sus características ventajosas, que incluyen:
Amplio rango dinámico:Capaz de medir amplitudes de vibración muy pequeñas y muy grandes.
Rango de frecuencia amplia:Puede capturar con precisión las vibraciones en un amplio espectro de frecuencias.
Excelente linealidad:Proporciona una salida eléctrica proporcional a la aceleración de entrada.
Alta estabilidad:Ofrece mediciones consistentes y confiables a lo largo del tiempo.
Instalación relativamente conveniente:Se puede montar utilizando varios métodos dependiendo de la aplicación.
Para aprovechar todo el potencial de su acelerómetro y garantizar las mediciones de vibración precisas, adhiera a los siguientes principios y métodos de instalación:
I. Principios de instalación: establecer la base para la precisión
Para un rendimiento óptimo, observe estas reglas fundamentales al instalar su acelerómetro:
a) Ubicación estratégica:Coloque el acelerómetro lo más cerca posible del punto de prueba específico en la estructura para garantizar que experimente el mismo movimiento que el área que se analiza.
b) Montaje seguro y firme:El acelerómetro y su superficie de montaje deben ser lo más rígidos y firmemente conectados como sea posible. La superficie de montaje debe estar limpia y plana para garantizar el máximo contacto y la ruta de transmisión más directa o más corta de la vibración. Para acelerómetros uniaxiales, alinee cuidadosamente la dirección de detección (eje principal) con la dirección de interés.
c) Minimizar los efectos de carga de masa:La introducción del acelerómetro debe causar una alteración mínima al movimiento de la estructura de prueba. Emplee técnicas de montaje simétricos cuando sea posible para minimizar la distorsión del movimiento. La masa del acelerómetro y cualquier hardware de montaje debe ser significativamente menor que la masa dinámica de la estructura medida (idealmente una relación de masa de menos de 1/10 para pequeños objetos de luz).
d) Evitar la interferencia de resonancia:La frecuencia de funcionamiento máxima de su prueba debe ser significativamente menor que la frecuencia de resonancia de montaje del acelerómetro elegido. Operar cerca de la resonancia de montaje puede conducir a lecturas amplificadas e inexactas.
E) Gestión de cables:Cuando se usan acelerómetros conectados axialmente, los cables rígidos pueden inducir la tensión en la carcasa, lo que puede afectar las mediciones. Aprieta de forma segura el cable cerca del acelerómetro para evitar esto. Para los acelerómetros piezoeléctricos, los cables sueltos pueden generar ruido triboeléctrico (electricidad estática friccional).
(Diagrama que muestra el acelerómetro de plomo axial y el acelerómetro de plomo lateral) (Leyenda para el diagrama: 1 - No sujeto a la fuerza, 2 - Superficie de conexión del cuerpo vibrante, 3 - Asegure el cable a la superficie vibratoria)
f) Aislamiento eléctrico:Los acelerómetros tienen diferentes propiedades de aislamiento eléctrico. Algunos tienen bases aisladas incorporadas, mientras que otros requieren tornillos de montaje aislados y lavadoras de mica para evitar bucles de tierra en el sistema de medición. El uso de tornillos aislados con lavadoras de mica en los puntos de contacto es una forma efectiva de resolver problemas de bucle de tierra.
II. Métodos de instalación específicos: aplicación práctica
Aquí hay un desglose de los métodos comunes de instalación del acelerómetro:
a. Montaje de tornillo:
(Diagrama que muestra una curva de respuesta de frecuencia típica para un acelerómetro montado en el tornillo con grasa) (Leyenda para el diagrama: curva de respuesta de frecuencia típica de un tornillo de acelerómetro montado con grasa (en relación con la aceleración absoluta de la estructura en el punto de conexión)))
Preparación de la superficie:La superficie de montaje tanto en el acelerómetro como en la estructura de prueba debe estar limpia, plana y mecanizada suavemente, cumpliendo con las especificaciones recomendadas del fabricante. El orificio del tornillo de montaje debe ser perpendicular a la superficie de montaje.
Aplicación de par:Apriete el tornillo de montaje al par recomendado por el fabricante para lograr una conexión segura sin dañar el acelerómetro.
Medio de acoplamiento:Aplique una capa delgada de aceite o grasa entre las superficies de apareamiento para mejorar el contacto y maximizar la rigidez, mejorando la respuesta de alta frecuencia.
Longitud del tornillo:Asegúrese de que el tornillo no gire en el orificio tocado, ya que esto puede crear un pequeño espacio entre las superficies de montaje, reduciendo la rigidez.
b. Enlace adhesivo:
Este método es adecuado cuando no es factible los agujeros de perforación en la estructura de prueba, se requiere aislamiento eléctrico o la superficie de montaje tiene una planitud insuficiente. Los tornillos de montaje adhesivo (espárragos con roscas en un extremo y una plataforma de unión en el otro) también se usan comúnmente.
(Diagrama que muestra una curva de respuesta de frecuencia típica para un acelerómetro adhesivamente unido) (Leyenda para el diagrama: curva de respuesta de frecuencia típica de un acelerómetro adhesivamente unido (en relación con la aceleración absoluta de la estructura en el punto de conexión))))
Limpieza de superficie:Limpie las superficies de unión de acuerdo con las recomendaciones del fabricante del adhesivo.
Capa adhesiva delgada:Aplique el adhesivo para formar una película delgada, que idealmente debería actuar como un resorte rígido para una respuesta de frecuencia óptima.
Selección de adhesivo:A menudo se usan adhesivos acrílicos o termoestables. Evite los adhesivos blandos o aquellos que retienen una flexibilidad significativa después de la evaporación del solvente, ya que pueden reducir la frecuencia resonante. Los adhesivos de cianoacrilato (súper pegamento como 502) ofrecen una respuesta de frecuencia amplia, pero no son adecuadas para todas las aplicaciones y pueden contaminar las roscas de tornillo. Antes de la aplicación, limpie la superficie de montaje con un disolvente de hidrocarburos, manteniendo el solvente lejos de los cables y conectores. Presione el sensor firmemente en el adhesivo rápidamente para lograr una línea de enlace delgada. También se deben considerar las limitaciones de temperatura del adhesivo.
do. Dispositivos de montaje:
Los dispositivos de montaje, incluidos los tornillos aislados eléctricamente, deben ser rígidos, livianos, tienen un pequeño momento de inercia y ser estructuralmente simétricos sobre el eje de detección. Evite usar soportes siempre que sea posible. Si es necesario, opte por cubos de metal pequeños y rígidos montados de forma segura a la estructura con superficies mecanizadas y agujeros tocados para la conexión de tornillo.
d. Otros métodos de montaje:
Las técnicas de montaje alternativas incluyen el uso de una capa delgada de cera de abejas solidificada, cinta adhesiva de doble cara, bases magnéticas, abrazaderas de montaje rápido y bases de montaje de vacío.
(Diagrama que muestra una curva de respuesta de frecuencia típica para un acelerómetro montado en la cera de abejas) (Leyenda para el diagrama: curva de respuesta de frecuencia típica de un acelerómetro montado con una capa delgada de cera de abejas (en relación con la aceleración absoluta de la estructura en el punto de conexión)))
Montaje de cera de abejas:Adecuado para aplicaciones de temperatura ambiente con sensores que pesan menos de 100 gramos. Es conveniente pero limita la temperatura de funcionamiento a menos de 40 ° C y es adecuado para niveles de aceleración más bajos.
(Diagrama que muestra una curva de respuesta de frecuencia típica para un acelerómetro montado en cinta de doble cara) (Leyenda para el diagrama: curva de respuesta de frecuencia típica de un acelerómetro montado con cinta de doble cara)
Montaje de cinta de doble cara:Varios tipos de cintas de doble cara ofrecen diferentes temperaturas de funcionamiento y espesores. Elija una cinta apropiada para su aplicación.
(Diagrama que muestra una curva de respuesta de frecuencia típica para un acelerómetro magnético montado en la base) (Leyenda para el diagrama: curva de respuesta de frecuencia típica de un acelerómetro montado con una base magnética)
Montaje de base magnética:Conveniente para mediciones rápidas en superficies ferromagnéticas, pero limita el nivel máximo de vibración y la frecuencia de medición. Este método generalmente reduce la frecuencia de resonancia de montaje a alrededor de 7 kHz, reduciendo el rango de frecuencia utilizable a aproximadamente 2 kHz (alrededor de 1/3 de la resonancia de montaje). Las bases magnéticas también agregan una masa significativa y tienen una fuerza de retención limitada, típicamente adecuada para aceleraciones por debajo de 200 g.
Iii. Precauciones importantes: garantizar la longevidad y la integridad de los datos
Tenga en cuenta estos puntos cruciales al manejar y usar acelerómetros:
a) eliminación suave:Al desmontar sensores, corte suavemente cualquier adhesivo o cera de abejas del lado en lugar de tirar directamente de la superficie de montaje, lo que puede dañar el sensor.
b) Precaución de unión directa:La unión directa de la mayoría de los acelerómetros sin una consideración adecuada para la eliminación y el daño potencial generalmente no se recomienda.
c) Seguridad de cable para acelerómetros de tipo de carga:Asegúrese de que los cables de acelerómetro de tipo de carga estén de forma segura. El movimiento, la flexión o el estiramiento de estos cables durante la medición pueden causar cambios en la capacitancia local y la carga entre el conductor y el escudo, introduciendo un ruido significativo. Los acelerómetros IEPE (piezoeléctricos electrónicos integrados) con amplificadores incorporados son mucho menos susceptibles al ruido de cable.
d) Integridad del conector:Cuando use múltiples cables de extensión, asegúrese de que los conectores se mantengan limpios y libres de polvo, agua o contaminantes conductores.
e) Carga de masa en objetos de luz:Para objetos pequeños y livianos (por ejemplo, cuchillas pequeñas), considere cuidadosamente el efecto de carga de masa del acelerómetro. Apunte a una relación de masa del acelerómetro al objeto de prueba de menos de 1/10.
f) Evite dejar caer:Nunca deje caer el sensor en superficies duras, ya que esto puede causar un daño irreparable.
g) Límites de temperatura:Siempre opere sensores dentro de su rango de temperatura especificado para evitar daños y garantizar mediciones precisas.
Al cumplir con estas pautas de instalación y precauciones de uso, puede maximizar la precisión, la confiabilidad y la vida útil de sus acelerómetros, asegurando datos de alta calidad para sus esfuerzos de prueba de vibración. En Dongguan Precision, estamos dedicados a proporcionarle no solo sistemas de prueba de vibración avanzados sino también el conocimiento para utilizarlos de manera efectiva.
Mantenimiento de su cámara de ensayo ambiental: asegurar longevidad y resultados confiables
En Dongguan Precision Test Equipment Co., Ltd., entendemos que su cámara de prueba ambiental es una inversión crucial para garantizar la calidad y fiabilidad de sus productos.Para maximizar su vida útilEsta guía describe los principales procedimientos de mantenimiento para su cámara de ensayo ambiental:
1Gestión dedicada y profesional:
Para una atención óptima, recomendamos encarecidamente asignar personal dedicado y capacitado para administrar y mantener su cámara de prueba.Invertir en la formación profesional del proveedor de equipos equipará a su equipo con los conocimientos y habilidades especializados necesarios para un mantenimiento y una solución de problemas eficaces.
2Limpieza trimestral del condensador:
Sistemas refrigerados por aire:Inspeccionar y limpiar regularmente (cada tres meses) el ventilador del condensador y eliminar el polvo o los desechos acumulados en las aletas del condensador para garantizar un flujo de aire adecuado y un intercambio de calor eficiente para el compresor.
Sistemas refrigerados por agua:Además de mantener la presión y la temperatura correctas del agua de entrada, asegúrese de que el caudal de agua especificado se proporcione constantemente.programación trimestral de la eliminación de escamas y limpieza de los componentes internos del condensador para evitar la acumulación de escamas y mantener una transferencia de calor óptima.
3. Limpieza trimestral del evaporador (deshumidificador):
Debido a la circulación forzada de aire dentro de la cámara de ensayo y a los diferentes niveles de limpieza de las muestras de ensayo, el polvo y las partículas pueden acumularse en el evaporador (bobinas del deshumidificador).Un programa de limpieza regular (cada tres meses) es vital para mantener un intercambio de calor eficiente para el enfriamiento y la deshumidificación.
4. Limpieza y equilibrio de las palas de los ventiladores de circulación y de los ventiladores de condensador:
Al igual que el evaporador, las cuchillas del ventilador de circulación y las cuchillas del ventilador de condensador pueden acumular polvo y escombros dependiendo del entorno de funcionamiento de la cámara.Es necesario limpiar con regularidad para asegurar un flujo de aire adecuadoAdemás, compruebe periódicamente si hay algún desequilibrio en las palas del ventilador, lo que puede provocar vibraciones y daños potenciales.
5. Mantener un entorno ambiente óptimo:
Las cámaras de ensayo medioambientales son instrumentos de precisión y a menudo representan una inversión significativa.Recomendamos colocarlos en un ambiente con temperatura ambiente controlada, idealmente entre 8°C y 23°C. Para los laboratorios que no puedan cumplir estas condiciones,se recomienda encarecidamente la instalación de un aire acondicionado adecuado (para las unidades refrigeradas por aire) o una torre de refrigeración (para las unidades refrigeradas por agua).
6. Limpieza del circuito de agua y del humidificador:
Un flujo de agua restringido o una acumulación de escamas en el humidificador pueden provocar una combustión en seco y daños potenciales en el elemento de calefacción.Es imperativo limpiar regularmente las líneas de agua y el humidificador para garantizar un suministro de agua sin obstáculos y una humidificación eficiente..
7Rutinaria después de la prueba:
La adopción de un procedimiento consecuente después de los ensayos es una práctica de mantenimiento sencilla pero eficaz.establecer la temperatura de la cámara en condiciones cercanas al ambiente y dejar que funcione durante aproximadamente 30 minutos antes de apagarla.Por último, limpie las paredes interiores del espacio de trabajo para eliminar cualquier humedad residual o contaminantes.
8Principios de solución de problemas:
Las cámaras de ensayo ambientales son sistemas complejos que comprenden componentes eléctricos, de refrigeración y mecánicos.Es esencial un enfoque sistemático e integral para la resolución de problemas.
Desde el exterior al interior:Comience por eliminar factores externos como el suministro de agua de refrigeración y los problemas de suministro de energía.
Análisis sistemático:Una vez descartados los factores externos, adopte un enfoque basado en el sistema.
Deducción lógica:Un método inverso de solución de problemas puede ser eficaz: primero compruebe los diagramas de cableado eléctrico para detectar posibles fallos en el sistema eléctrico y luego investigue el sistema de refrigeración.
Precauciones antes de desmontar:Nunca trate de desmontar o reemplazar a ciegas los componentes sin comprender claramente el fallo.
9Protocolo de inactividad a largo plazo:
Si la cámara de ensayo debe dejarse fuera de servicio durante un período prolongado, se recomienda encenderla durante al menos una hora cada dos semanas.Esto ayuda a la circulación de los fluidos internos y previene posibles problemas derivados de la inactividad prolongada..
10Relocación segura:
La reubicación de una cámara de ensayo medioambiental debe realizarse idealmente bajo la guía de nuestro personal técnico cualificado.Esto minimizará el riesgo de daños accidentales o mal funcionamiento durante el proceso de mudanza.
Al cumplir con estas pautas de mantenimiento, puede extender significativamente la vida útil de su cámara de pruebas ambientales Dongguan Precision,garantizar la exactitud y fiabilidad de los resultados de sus pruebasPara cualquier consulta específica de mantenimiento o para programar un servicio profesional, no dude en ponerse en contacto con nuestro equipo de soporte.
En Dongguan Precision Test Equipment Co., Ltd., entendemos la importancia primordial de la seguridad y confiabilidad del producto en varias industrias. Para ayudar a los fabricantes a garantizar que sus productos cumplan con los estrictos estándares de calidad y resistir las condiciones del mundo real, ofrecemos una gama integral de cámaras de pruebas ambientales diseñadas para cumplir con una multitud de estándares de pruebas internacionales y nacionales. Este documento sirve como guía para los estándares de prueba clave que nuestro equipo está construido para cumplir, particularmente enfocándose en el área crítica deNuevas pruebas de batería de energíay otras simulaciones ambientales esenciales.
I. alimentar el futuro de manera segura: nuevos estándares de prueba de batería de energía
La seguridad y el rendimiento de las nuevas baterías energéticas son críticos. Nuestras cámaras de prueba están diseñadas para facilitar las pruebas de acuerdo con los siguientes estándares clave:
Prueba de impacto mecánico:
UL 1642: Estándar para baterías de litio - Pruebas mecánicas - Prueba de impacto
UL 2054-2005: Batterías domésticas y comerciales - Pruebas mecánicas - Prueba de impacto
ONU 38.3: Recomendaciones sobre el transporte de productos peligrosos - Manual de pruebas y criterios - Sección 38.3 - Prueba de impacto
GB/T 18287-2000: Especificación general para baterías de iones de litio para teléfonos celulares - Prueba de impacto de objetos pesados
SJ/T 11169-1998: Estándar para baterías de litio - Prueba de impacto
YD 1268-2003: Requisitos de seguridad y métodos de prueba para baterías de litio y cargadores para teléfonos de comunicación móvil - Prueba de impacto
SJ/T 11170-1998: Estándar de seguridad para baterías domésticas y comerciales - Pruebas mecánicas - Prueba de impacto
PRUEBA DE APTIR (APROBA):
GB/T 2900.11-1988: Especificación de inspección de rendimiento de seguridad para baterías de iones de litio para lámparas de mineros - trituración
YD 1268-2003: Requisitos de seguridad y métodos de prueba para baterías de litio y cargadores para teléfonos de comunicación móvil - rendimiento de resistencia a la de aplastamiento
SJ/T 11169-1998: Estándar para baterías de litio - Prueba de aplastamiento
UL 1642: Estándar para baterías de litio - Prueba de compresión
GB/T 8897.4-2002: Batterías primarias - Parte 4: Seguridad de las baterías de litio - trituración
SJ/T 11170-1998: Estándar de seguridad para baterías domésticas y comerciales: aplastamiento
YDB 032-2009: Paquetes de baterías de iones de litio de respaldo para uso de la comunicación: resistencia a la extrusión
UL 2054: Estándar para baterías domésticas y comerciales - Prueba de compresión
QB/T 2502-2000: Especificación general para baterías recargables de iones de litio - prueba de trituración (cortocircuito interno)
Prueba de punción (penetración de uñas):
GB/T 18332.2-2001: Batinas recargables de hidruro de níquel -metal para vehículos eléctricos de carretera - Prueba de punción
MT/T 1051-2007: Batterías de iones de litio para lámparas de mineros - Prueba de penetración de uñas
II. Simulando diversas condiciones climáticas: pruebas de alta temperatura y humedad
NuestroCámaras de prueba de temperatura alta y baja,Cámaras de prueba de temperatura y humedad constante, yCámaras de prueba de humedad de alta y baja temperaturaestán diseñados para cumplir con los requisitos de los siguientes estándares, asegurando una evaluación de rendimiento confiable bajo varias tensiones climáticas:
GB/T 5170.5-2008
GB/T 10586-2006
GB/T 2423.1-2008 (prueba A: frío)
GB/T 2423.2-2008 (prueba B: calor seco)
GB/T 2423.3-2006 (prueba CA: calor húmedo en estado estacionario)
GB/T 2423.4-2008 (DB de prueba: alterar calor húmedo)
Iii. Cambios de temperatura rápidos resistentes: prueba de choque térmico
NuestroCámaras de prueba de choque térmicoestán diseñados para sujetar productos a variaciones de temperatura rápidas y extremas, adheriendo y satisfaciendo los requisitos de los siguientes estándares:
GB/T 2423.1-2001: Pruebas ambientales para productos eléctricos y electrónicos - Parte 2: Métodos de prueba - Prueba A: frío
GB/T 2423.2-2001: Pruebas ambientales para productos eléctricos y electrónicos - Parte 2: Métodos de prueba - Prueba B: calor seco
GB/T 2423.22-1989: Pruebas ambientales para productos eléctricos y electrónicos - Parte 2: Métodos de prueba - Prueba N: Cambio de temperatura
GJB 150.3-86: Métodos de prueba ambiental para equipos militares: prueba de baja temperatura
GJB 150.4-86: Métodos de prueba ambiental para equipos militares: prueba de alta temperatura
GJB 150.5-86: Métodos de prueba ambiental para equipos militares - Prueba de choque de temperatura
GJB 360.7-87: Métodos de prueba para componentes electrónicos - Método 405: Prueba de choque de temperatura
GJB 367.2-87: Métodos de prueba para equipos electrónicos: prueba de choque de temperatura 405
SJ/T 10187-91: Cámaras de prueba de ciclo de temperatura de la serie Y73 - Tipo de cámara única
SJ/T 10186-91: Cámaras de prueba de ciclo de temperatura de la serie Y73: dos cámaras
IEC 68-2-14: Pruebas ambientales - Parte 2: Pruebas - Prueba N: cambio de temperatura
GB/T 2424.13-2002: Pruebas ambientales para productos eléctricos y electrónicos - Parte 2: Métodos de prueba - Orientación para pruebas de ciclo de temperatura
GB/T 2423.22-2002: Prueba ambiental - Parte 2: Métodos de prueba - Prueba N: cambio de temperatura
QC/T 17-92: Reglas generales para la prueba de meteorización de piezas automotrices
EIA 364-32: Procedimiento de prueba de choque térmico (ciclo de temperatura) para conectores eléctricos y enchufes Evaluación de efectos ambientales
IV. Análisis de fallas de aceleración: cámaras de pruebas de vida altamente aceleradas (HAST)
NuestroCámaras de pruebas de vida altamente aceleradas (HAST)están diseñados para acelerar el proceso de envejecimiento de los productos bajo condiciones controladas de alta temperatura y alta humedad, que cumple con:
GB/T 5170.2-1996: Equipo de prueba ambiental para productos eléctricos y electrónicos - Parte 2: Cámaras de temperatura
IEC 60068-2-66-1994: Pruebas ambientales - Parte 2-66: Pruebas - Prueba CY: calor húmedo, estado estacionario, prueba acelerada principalmente destinada a componentes
V. Evaluación de la resistencia a la luz solar: cámaras de prueba de meteorización ultravioleta
NuestroCámaras de prueba de meteorización ultravioletaSimule los efectos dañinos de la luz solar, la lluvia y el rocío para evaluar la durabilidad de los materiales expuestos a entornos al aire libre, cumpliendo con los requisitos de estándares como:
ASTM G154: Práctica estándar para operar aparato de lámpara ultravioleta fluorescente (UV) para la exposición de materiales no metálicos
AstmD4587-91:
ISO 11507/4892-3: Plastics - Fuentes de luz de laboratorio - Parte 3: Lámparas UV fluorescentes
NE 927-6
ASTM G 153: Práctica estándar para operar aparatos de luz de arco de carbono cerrado para la exposición de materiales no metálicos
AstmD 4329: Práctica estándar para la exposición fluorescente UV de plásticos
ASTM D 4799: Práctica estándar para condiciones de prueba de meteorización acelerada para materiales bituminales (método de arco de xenón)
AstmD 4587: Práctica estándar para realizar determinaciones de resistencia a los fluidos industriales
SAE J 2020: Exposición acelerada de materiales exteriores automotrices utilizando un aparato fluorescente de UV y condensación
ISO 4892:
VI. Su socio en cumplimiento y confiabilidad: Dongguan Precision
En Dongguan Precision Test Equipment Co., Ltd., estamos comprometidos a proporcionar cámaras de prueba ambientales confiables y de alta calidad que permitan a los fabricantes a satisfacer las estrictas demandas de varias industrias. Nuestro equipo está diseñado con ingeniería de precisión y se adhiere a una amplia gama de estándares de pruebas nacionales e internacionales, asegurando la seguridad, el rendimiento y la longevidad de sus productos.
Contáctenos hoy para discutir sus requisitos de pruebas específicos y descubrir cómo nuestras soluciones integrales pueden ayudarlo a lograr el cumplimiento y generar una mayor confianza en la confiabilidad de sus productos.
I. Comprensión de las pruebas de choque térmico de los PCB
Concepto: ensayo de choque térmico, también conocido como ciclo de temperatura o ensayo de resistencia térmica,Simula los rápidos cambios de temperatura o los ambientes de altas y bajas temperaturas que un producto puede experimentar durante su ciclo de vida.
Principio:Durante estos cambios bruscos de temperatura o extremos alternos, los diversos materiales que componen un PCB incluyendo el sustrato, prepreg (PP), revestimiento de cobre,y la máscara de soldadura se extienden y contraenEl estrés resultante y las diferencias en el coeficiente de expansión térmica (CTE) de estos materiales pueden conducir a daños físicos, degradación y cambios en la resistencia eléctrica dentro del PCB.
II. La importancia de las pruebas de choque térmico para los PCB
Las pruebas de choque térmico desempeñan un papel vital durante todo el ciclo de vida de un PCB:
Detección temprana de defectos de diseño (etapa de I+D):La identificación y rectificación de las deficiencias de diseño en el PCB en la fase de investigación y desarrollo evita problemas costosos más adelante, lo que acorta el ciclo de desarrollo y reduce los gastos generales.
Control de calidad en la fabricación:Evaluar si la calidad de los PCB fabricados cumple los requisitos del cliente.La detección temprana de defectos en el proceso de fabricación permite una investigación y mejora oportunas, garantizando la seguridad y la calidad de los productos enviados.
Validación de materiales y procesos:Evaluación de la fiabilidad de los materiales de base, las máscaras de soldadura, los prepreg y los procesos de fabricación para determinar su idoneidad para el entorno previsto del producto.
Comparación de materiales y procesos:Comparar la resistencia al choque térmico de los PCB fabricados con diferentes materiales y procesos para identificar opciones superiores.
III. Parámetros del equipo
Nuestras cámaras de choque térmico en Dongguan Precision están diseñadas para ofrecer pruebas precisas y confiables:
Parámetro
Especificación
Volumen interno nominal
300 litros
Rango de temperatura de ensayo
-70 °C ~ 200 °C
Fluctuación de la temperatura
≤ 1°C
Desviación de la temperatura
Las condiciones de ensayo de las pruebas de ensayo deberán ser las siguientes:
Tasa de calentamiento (cámara de alta temperatura)
≥ 11°C/min
Tasa de enfriamiento (cámara de baja temperatura)
≥ 5 °C/min
Peso máximo de la muestra
10 kg de peso
IV. Estudios de casos: Pruebas de choque térmico de PCB en el mundo real
Estudio de caso 1: Tabla de prueba de conteo de capas altas
Una placa de ensayo de alto recuento de capas se sometió a pruebas de choque térmico en línea para verificar el rendimiento del material de sustrato seleccionado en función de las especificaciones del cliente.Las condiciones y requisitos de ensayo fueron los siguientes::
Punto de ensayo
Condiciones de ensayo
Requisitos de las pruebas
Choque térmico (en línea)
-55°C/15min, 125°C/15min, 1000 ciclos
1. Tasa de cambio de resistencia ≤ 5%2En el análisis de la sección transversal no se observaron delaminados, agrietamientos de los tableros o de las barricas.
Gráfico de la curva de variación de la tasa de resistencia
Visión seccional de la posición de ensayo 1 Visión seccional de la posición de ensayo 3
Resultado:Después de la prueba, la tasa de cambio de resistencia en algunos puntos de prueba superó el 5%.Esto indicó una posible debilidad en la capacidad del material de sustrato para resistir la tensión inducida por los extremos de temperatura repetidosLos hallazgos llevaron a una reevaluación de la selección del material de sustrato para esta aplicación de alto recuento de capas.
Estudio de caso 2: Tabla de ensayo para automóviles
Una placa de ensayo automotriz fue sometida a pruebas de choque térmico para validar el rendimiento del material de la máscara de soldadura frente al cliente
Las condiciones y requisitos de ensayo fueron los siguientes:
Punto de ensayo
Condiciones de ensayo
Requisitos de las pruebas
Prueba de choque térmico
-40°C/15min, 125°C/15min, 500 ciclos
No se observaron ampollas, delaminación o grietas en la máscara de soldadura1. IPC-TM-650 2.6.7.1A Resistencia al choque térmico del revestimiento conformal2. IPC-TM-650 2.6.7.2C Choque térmico, ciclo térmico y continuidad3. IPC-TM-650 2.6.7.3 Resistencia al choque térmico de las máscaras de soldadura
Diagrama de observación después del ensayo
V. Condiciones comunes de ensayo de choque térmico
Las condiciones de ensayo específicas para los ensayos de choque térmico varían según la aplicación y las normas de la industria.
Tipo de muestra
Baja temperatura (°C)
Temperatura alta (°C)
Tiempo de retención (min)
Ciclos
Automóvil
-40 años.
125
¿ Qué es esto?
500
- 55 años
140
1000
- 65 años.
150
1500
Número de capas altas
-40 años.
125
¿ Qué es esto?
250
- 55 años
125
500
Alta frecuencia
-40 años.
125
15
500
Envase Substrato
- 55 años
150
30
1000
VI. Condiciones normalizadas de referencia (tableros impresos)
Punto de trabajo
Calificación
Pruebas de conformidad/aceptación de la calidad
Condiciones de horneado
(105 ~ 125)°C/ 6 horas
Soldadura por reflujo
6 veces el IR
Temperatura de ensayo (baja)
Negociado entre proveedor y comprador
-40°C, -55°C (por defecto), -65°C
Temperatura de ensayo (alta)
Negociado entre proveedor y comprador
Min: Tg-10°C (TMA) / Temperatura máxima de reflujo -25°C / 210°C
Tasa de cambio de temperatura de la muestra
> 10°C/min (también transición caliente y fría)
> 1°C/S (transición tanto caliente como fría)
Ciclos de ensayo
Negociado entre proveedor y comprador
100
Tasa de cambio de la resistencia
Negociado entre proveedor y comprador
El 5%
VII. Condiciones normalizadas de referencia (revestimiento conformado y máscara de soldadura)
Nivel
Baja temperatura (°C)
Temperatura alta (°C)
Tiempo de retención (min)
Ciclos
Las observaciones
1
-40 años.
125
15
100
Condición de ensayo predeterminada cuando no se especifique ningún requisito
2
- 65 años.
125
15
100
3
- 65 años.
250
15
100
Resultado:El examen microscópico después de la prueba reveló grietas en la máscara de soldadura en las esquinas de las almohadillas.Esto indicaba una flexibilidad o adhesión insuficientes del material de la máscara de soldadura para resistir las tensiones térmicas encontradas en el entorno automotriz.Los resultados condujeron a una investigación sobre materiales alternativos de máscaras de soldadura con una mejor resistencia a los golpes térmicos para esta aplicación automotriz.
VIII. Conclusión: Colaboración con Dongguan Precision para pruebas de choque térmico fiables
Los estudios de caso ponen de relieve el papel crítico de las pruebas de choque térmico en la identificación de posibles debilidades en los materiales y diseños de PCB.Estamos comprometidos a proporcionar cámaras de choque térmico de alto rendimiento y apoyo de expertos para ayudar a nuestros clientes a evaluar a fondo la fiabilidad de sus PCBNuestro equipo está diseñado para precisión, repetibilidad y cumplimiento de los estándares de la industria.
Al comprender los principios de las pruebas de choque térmico y utilizar equipos fiables, los fabricantes pueden abordar de manera proactiva los posibles problemas,garantizar el rendimiento y la durabilidad a largo plazo de sus productos electrónicosContacte con Dongguan Precision hoy para discutir sus necesidades específicas de pruebas de PCB y descubrir cómo nuestras soluciones pueden beneficiar sus procesos de garantía de calidad.